Describe the Structure and Function of Mitochondria
They have a matrix space containing the enzymes of the citrate cycle and beta-oxidation enclosed by an inner membrane containing the 4 complexes of the electron transport chain ATP synthase and specific carriers for metabolites. The function of the mitochondria is to turn the sugar.

What Is The Structure And Function Of Mitochondria A Plus Topper
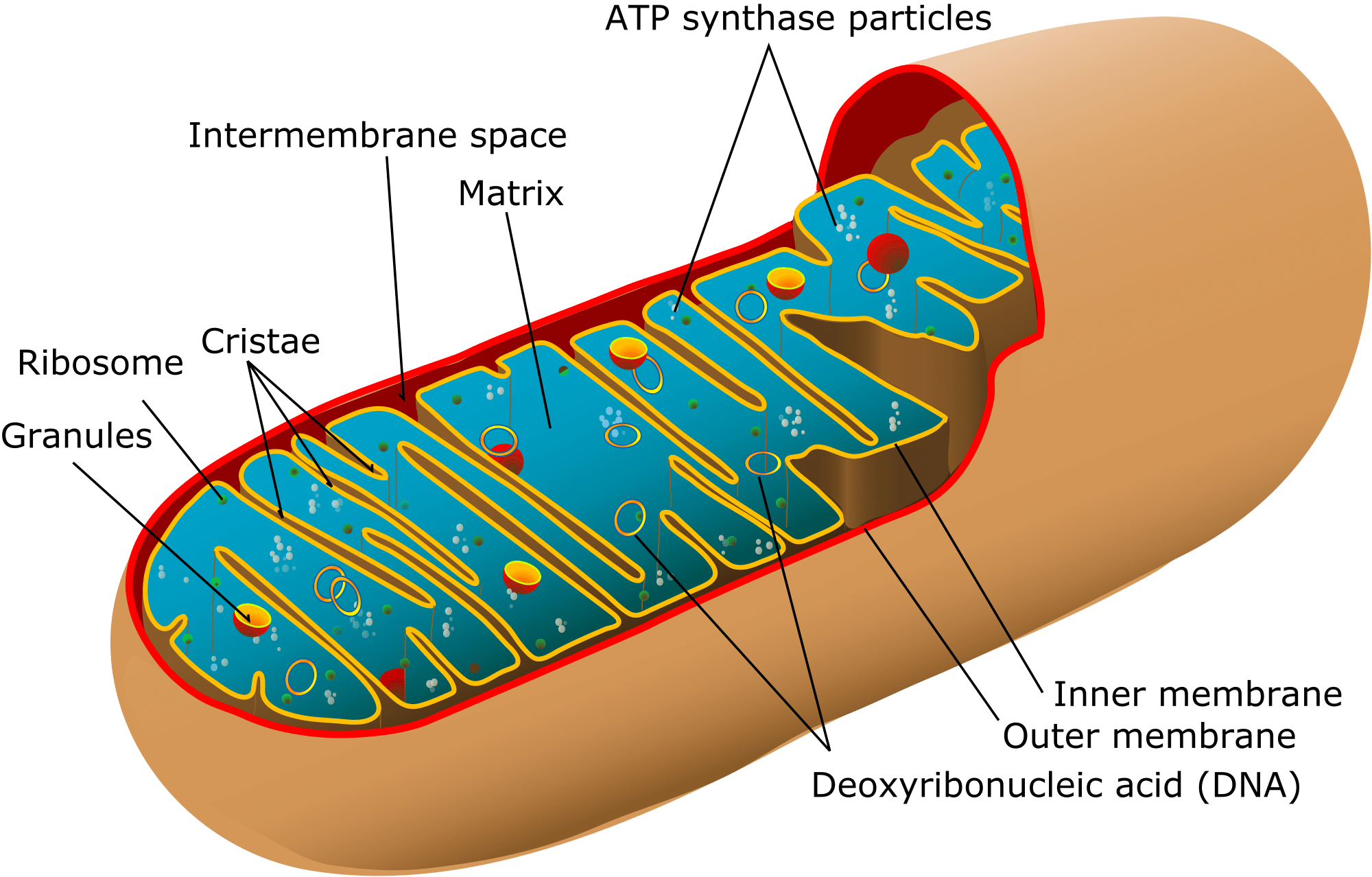
Mitochondria in animals are round or oval and are bound by a double membrane.

. Enzymes involved in the elongation of fatty acids and the oxidation of adrenaline can also be found on the outer. Functionconverts energy into a from the cell can use. Outline why the cell needs energy The cell then uses energy to carry out the essential life processes aka MRS C GREN Describe the shape of a mitochondrion Rod-shaped.
Mitochondrion are a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Double membrane bound organelles that are spherical to elongate in shape. Structure and function of mitochondria.
Mitochondria are the main site of ATP synthesis in aerobic cells using the free energy of the oxidation of metabolic fuels by oxygen. Mitochondria is regarded as the power house of the cell as it is the site of respiration. The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell ATP and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur.
The mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are associated with energy production or with the production of ATP. Mitochondrion is it is surrounded by a double membrane. They are rod-shaped structures that are enclosed within two membranes the outer membrane and the inner membrane.
The structure of the mitochondriasingular. It is enclosed by thinner membrane and is semi-rigid and gel-like consisting of a mixture of proteins and lipids. The simpler molecules of nutrition are sent to the mitochondria to be processed and to produce charged molecules.
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell as they produce cellular energy in the form of ATP to keep the individual cells and the plant functioning. The structural architecture and the organization into cellular compartments known as cell organelles enable eukaryotic cells to perform complex functions. The general formula for glucose oxidation is.
Functions of Mitochondria The most important function of mitochondria is to produce energy. Mitochondria is about 1 mm in diameter and 1-10 mm in length. Mitochondria-targeting antioxidants such as MitoQ appear to be promising for the preservation of vascular endothelial function with age and the prevention of CVD development.
F1 is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and Fo is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This process is. These membranes are made of phospholipid layers just like the cells outer membrane.
The different parts of mitochondria in animal cells are. Functions of Mitochondria The most important function of the mitochondria is to produce energy. 8 Structure of ATP synthase consists of two protein entities.
Popularly known as the Powerhouse of the cell mitochondria singular. These membranes are composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins. Describe the primary function of mitochondria Site of cellular respiration- the production of energy in the form of ATP from glucose.
The function of ATP synthase is to synthesise ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Structure of Mitochondria Mitochondria have two membranes an outer membrane and an inner membrane. They are the central executioner of cells and control cellular homeostasis through involvement in nearly all aspects of metabolism.
- Is mitochondria a. Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration. Structure Mitochondria have an inner and outer membrane with an intermembrane space between them.
Mitochondria are now known to be more than the hub of energy metabolism. The outer membrane contains proteins known as porins which allow movement of ions into and out of the mitochondrion. Describe the structure and functions of mitochondria.
Each mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound structure. The outer membrane covers the surface of the mitochondrion while the inner membrane is located within and has many folds called cristae. They are found inside the cytoplasm and essentially function as the cells digestive system.
Experimental studies showed that oxidative damage caused by mitochondria is the mechanism underlying the development of age-associated endothelial dysfunction. Step-by-step solution Step 1 of 5 The eukaryotic cells have complex structures and functions. The space in between the two membranes is called the inter-membrane space which has the.
The inner membrane form folds called the. Mitochondria produce the molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP one of the cells energy currencies that provide the energy to drive. It also contains looped mitochondrial DNA mitochondrial ribosomes and enzymes.
Mitochondria are made up of two membranes- the outer and the inner membrane. It is made up of protein and phospholipid bilayer. It has a diameter of 02-10μm and length 10-41μm.
As our understanding of mitochondria has expanded it has become clear that the structure function and pathology of the. The membranes are made up of phospholipids and proteins. These charged molecules combine with oxygen and produce ATP molecules.
Outer Membrane-The outer membrane keeps the inner organelles intact and in place. Proteasomes Large protein machines that break down proteins In cytosol and nucleus Bind proteins destined for degradation and use ATP hydrolysis to unfold the proteins and holds them in a chamber so the enzymes wo nt run rampant in the cell In eukaryotes Proteasomes act primarily on proteins that have been marked for destruction by the covalent attachment of a small. Mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cells.

Structure Of Mitochondria Biology Diagrams Cell Biology Mitochondria

Mitochondria Structure And Function With Diagram Mitochondria Structure And Function Oxidative Phosphorylation
Comments
Post a Comment